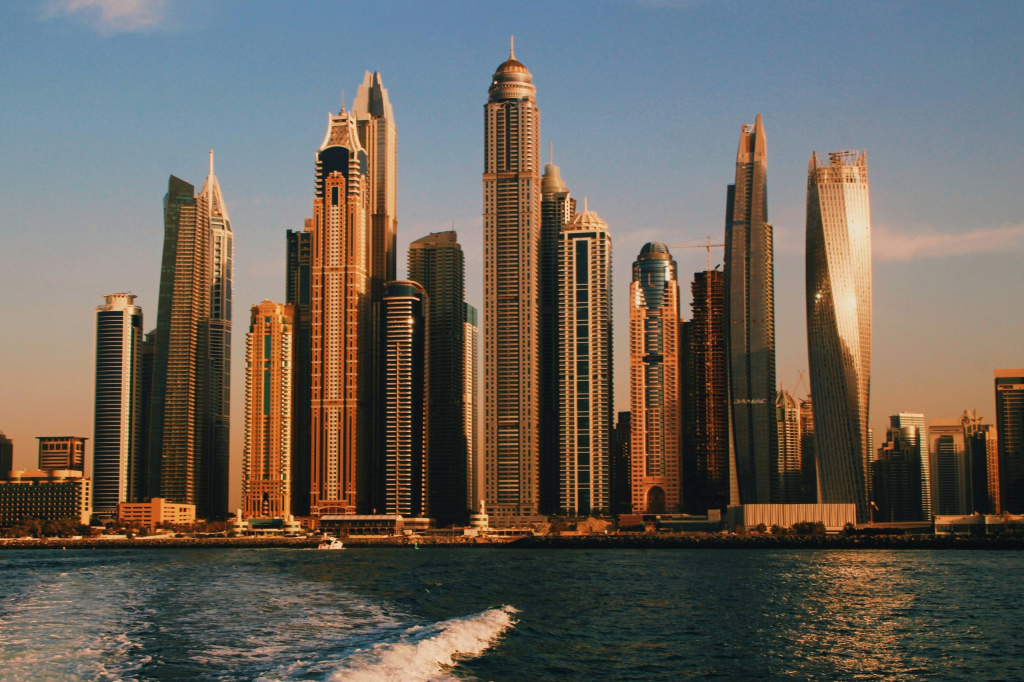
Dubai gets the attention of foreign property investors with zero federal or Emirate-level income taxes: the skyscrapers, palm-shaped islands, and the luxurious reputation of Dubai sound glamorous to many. The population is increasing, and the tourist hotspot stats as well. Moreover, Dubai has consistently famous development opportunities. Both now and the foreseeable future look promising for potential investors.
In this article, you can discover key areas in Dubai, average rental returns across property types, and the process of buying real estate as a foreigner in Dubai.
Let’s uncover Dubai’s global property environment.
Requirements for Buying a Property in Dubai
Buying a property in Dubai has a simpler process as of January 2024. The process now look like similar to purchasing real estate in most of the Western countries.
There are no age restrictions, and if you are a resident of the UEA, you are eligible to make an offer and acquire ownership of the property when you navigate the sales process successfully.
As a foreigner residing in the UEA, you can acquire freehold ownership without restrictions. Moreover, it does not matter if it is a freehold property contract, off plan properties, usefruct rights, or a leasehold up to 99 years.
Tax to Pay When Buying a Property in Dubai
Dubai’s real estate market offers some expected benefits: there is no need to pay taxes in a traditional sense.
While buying property in Dubai, you don’t need to pay tax on it in the traditional sense. The process is quite simple. As a buyer, you don’t need to pay income tax or inheritance tax on your property in Dubai. However, as you are a foreign investor, there might be an income tax from your country of residence if you do not actually live in Dubai.
Regarding taxes, it is important to be aware that you can pay the 4% transfer fee to the Dubai Land Department when a property is transferred to you. In addition to this fee, there will be a monthly housing fee, which is 5% of the area’s average rental value.
If you are an investor looking to discover the available property opportunities in the area, this means there is a potential for big profits.
If we compare, for example, you will pay taxes in many other countries based on a $700,000 property. Of course, the figures depend on the country and region of the property or its value as well.
Homeownership in Dubai
As a foreigner, you have the permit to own property in areas designed as freehold. If you are a foreigner but do not live in the UAE or an expatriate resident in Dubai, you have the right to acquire freehold ownership rights over property with no restriction. Plus, you are granted usufruct rights or leasehold rights for up to 99 years.
The property market and ownership dynamics in Dubai are changing and reshaping as tenants increasingly transition into becoming property owners due to various factors.
Dubai has been an attractive destination for expats for many times. As the city offers a cosmopolitan lifestyle, tax-free benefits, and diverse career opportunities, many expats prefer moving to Dubai for the short or long term. Beyond renting an apartment, many expats plan to become homeowners in Dubai.
History and Overview of the Property Market in Dubai
The government implemented visionary initiatives in Dubai in the early 2000s, so the real estate market has roots back more than 20 years. The government aimed to diversify the economy and attract foreign investment. In 2002, they announced the freehold ownership laws, opening doors for international buyers. In the end, these efforts were made to let foreign buyers own property in designated areas.
They were ambitious projects, innovative architectural designs to boost the real estate market, and international investment in the country. These initiatives ended with iconic developments in Dubai, such as the Palm Jumeirah, Burj Khalifa, and Dubai Marina. They all captured global attention and established a symbol of modern luxury in the UAE’s famous city, Dubai.
The government’s focus is on becoming a world-class city followed by state-of-the-art transportation networks as well as an extensive metro system, and highways. Connectivity was the main goal of these projects, but adding value to the real estate market was aimed as well, finally creating new opportunities for development.
Economic Diversification: Beyond Oil
The role of Dubai’s real estate market is essential for the government’s strategy, diversifying the country’s economy away from oil dependency. Its vision is to transform Dubai into a global business hub. And the proven result is the establishment of free zones and business-friendly regulations. This way, Dubai attracts multinational corporations and entrepreneurs from all around the world. A surge in demand was created for office spaces and commercial properties. It further drove the growth of the real estate market.
Types of Property in Dubai
There is a wide range of properties to cater to every budget and preference. Single and small families might prefer apartments while aiming for a low-maintenance lifestyle. There are also villas available for more space and privacy if you prefer a luxurious lifestyle.
According to Dubai’s zoning regulations, the city is divided into zones, each designated for a specific type of land use. Some of the common property types in Dubai are residential, commercial, industrial, recreational, and mix-use zones.
Residential property means a residence where an individual or a family lives. It can include singe-family homes, multi-family homes, condos, and mobile homes. You can find residential properties in different styles, such as bungalows, two-story houses, or cabins.
Single-Family Homes in Dubai
Single-family homes are built to accommodate one family, with only one kitchen and one set of utilities.
Multi-family Homes in Dubai
Multi-family homes, on the other hand, accommodate multiple families under the same roof so they can live separately from each other. Within the unit, you can have your own kitchen, address, entrance, and utilities. Moreover, multi-family properties can be called duplexes, triplexes, or quatriplex. It is up to the number of units within the property to call it multi-family property. Generally, there is one owner of those properties, and it can be an individual.
Condos in Dubai
Condos are units within a residential complex, and they hold a number of separate units, each owned by an individual or family. The responsibility of the maintenance and repair belong to the condo owners as they own the property.
Mobile Homes in Dubai
Mobile homes are designed as single-family homes that are built in a factory. And they are attached to a permanent chassis before the homes are being transported to their permanent location. You can use these residential properties if you are seeking residence. So these properties cannot be used as a type of business or industry.
Commercial property in Dubai
You can buy a property in Dubai on a freehold basis if you are a foreigner. If you want to buy a commercial property in Dubai, you need a valid trade license.
What is Required To Buy Real Estate in Dubai as a Foreigner?
If you are a foreigner, you can also gain freehold ownership without limits, whether it is through a freehold property contract, off-plan properties , usufruct rights, or a 99-year leasehold. Also, you do not neet to have a visa for this. Let’s see the steps to follow for buying real estate in Dubai as a foreigner.
Step 1: Prepare the Buyer/Seller Contract
When you’ve found the appropriate home, contact the seller to discuss conditions. You can choose to pay in cash or take out a mortgage. While a real estate agent or lawyer is not required at this stage, drafting a detailed contract is critical.
Step 2: Sign the Real Estate Sale Agreement
You may readily obtain the sale contract (Form F), known as a Memorandum of Understanding (MOU), from the Dubai Land Department’s (DLD) official website.
Additionally, you are able to insert your own terms in the contract. Once everything is in order, you and the seller should sign in front of a witness, preferably at the Registration Trustee’s office.
Furthermore, you need submit a 10% security deposit on the property to the Registration Trustee. You will receive after the transaction is complete.
Step 3: Apply for No Objection Certificate
At this stage, you will have a brief conversation with the developer to get a No Objection Certificate (NOC) and complete the ownership transfer. If there are no outstanding utility bills or charges on the property, the developer will provide the certificate.
Step 4: Transferring Ownership at the Registrar’s Office
You should send an authorized agent, come in person, or have the necessary paperwork ready. The transfer can be completed in a few simple steps.
If the parties turn in their paperwork ahead of time, the transfer will be completed that same day. In addition, a new title deed with your name as the new owner will be provided following receipt of the approval email.
Mortgages and Down Payments
For foreigners purchasing a home in Dubai, the minimum mortgage down payment is 20%; for locals, it is 15%. This implies that if the desired home’s price is AED 1 million, the amount of money you’ll need to pay in advance is AED 200k for foreigners and AED 150k for Emiratis.
What are the Lending Terms?
Both fixed-rate and variable-rate mortgages are offered in the United Arab Emirates. Although they might be as short as one year, fixed terms often last five years.
The Deposit or Down Payment
If an expat is purchasing a house up to AED 5 million, they will require a deposit of at least 25% when taking out a residential loan. Higher-end properties will demand a minimum 35% down payment.
Variable Rate Mortgage
| Deal type and length | Current average rate across all lenders | Current average rate across big six lenders |
| 2 year fixed-rate (75% LTV) | 5.89% | 5.14% |
| 5 year fixed-rate (75% LTV) | 5.44% | 4.74% |
| 2 year variable rate (75% LTV) | 5.84% | 5.75% |
| Standard variable rate (SVR) | 8.65% | 7.5% |
How to Qualify for a Mortgage in Dubai
Either a resident or a national of the UAE, making at least AED 15,000 each year is required. A foreign worker can be qualified for a mortgage who has worked in the UAE for three years or longer, with at least one year in your current role. Not more than 65 years old when the loan matures if you are salaried, or 70 years old if you work for yourself.
Required Documents for Mortgage
- a copy of your passport and visa.
- your Emirates ID in copy form.
- a pay certificate serving as employment verification.
- evidence of residency (a copy of the DEWA bill or the rental agreement)
- bank statements and pay stubs from the last six months.
- the most recent credit card statements.
Acquiring Home and Life Insurance
In the United Arab Emirates, obtaining a mortgage requires having life insurance. You will pay for life insurance in one form or another when you obtain a home loan in the United Arab Emirates, whether you realize it or not.
Even though Dubai is a safe country overall, homeowners must have a property insurance policy. Home insurance provides financial security against unanticipated occurrences like burglary, fire, and natural catastrophes.
Main Covers of Insurance
Protection against explosions, lightning, earthquakes, falling objects that have been placed, and loss or damage to contents during transit.
Comparing Dubai’s Real Estate Tax with Other Countries
UK: £18,700. It includes up to 12% stamp duty. In addition, it has up to 28% capital gains tax as an investor, as well as legal, inspection, and survey expenses.
USA: $31,500. This includes transfer fees of up to 2% of the property value, title insurance, attorney expenses, and appraisal fees.
Australia: $29,000. This includes stamp duty, which can be up to 5.5% of the property value, in addition to legal, application, and inspection fees.
Japan: $35,000, which includes a 3% tax on the property’s assessed value, a 2% licensing tax, estate agent costs, and a 3% city planning tax.
Dubai: $28,000 – that is all you have to pay.
We can understand from these comparisons that buying property in Dubai offers many opportunities to foreign investors, including good rental returns. Furthermore, investors can find the potential to make a great income from their property ownership in Dubai.
Finding a Property in Dubai
If you plan to look for a property for sale in Dubai, you can find many investment options through several websites. Or, you can have someone as a direct contact and work with a real estate agent to discover the investment properties.
Conclusion
Whether you’re looking for a luxurious home, a profitable investment, or a new destination to call your own, Dubai has a multitude of property alternatives. Freehold ownership provides you with complete control over your land and building, making it an appealing option for individuals looking for a long-term investment in this vibrant city.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I buy property in Dubai if I’m not a resident?
You need to simply hold a valid passport – a resident visa is not required. You can work with local real estate agents or directly with the developer to find the right property and complete the necessary formalities.
Can you own 100% property in Dubai?
Yes, you can own 100% of the property in Dubai in freehold areas with the need for a local partner.
Can I get Dubai citizenship if I buy a house?
No, the UAE does not award direct or indirect UAE citizenship by investment; it only awards residency. Instead of citizenship by investment, an investor visa (UAE passvisa) is available. The Dubai residence permit can be renewed.
How much does a house in Dubai cost?
As of February 2023, the average house price in Dubai is around AED 3.3 million.
What is the benefit of owning property in Dubai?
Dubai’s real estate market offers high rental yields compared to major cities like London, New York, or Hong Kong. The average return on investment (ROI) in Dubai varies between 6% and 10%, depending on factors like location, property type, and timing of investment.